DOL starter, also called Direct online Starter, is one of the simplest types of motor starters used to start an induction motor.
I can see DOL starters everywhere in my work (just for low-power motors).
In this article, I will answer 6 important questions for beginners about this starting method. Let’s dive directly into the questions.
Table of Contents
What is DOL starter?
A Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is a type of motor starter used for the starting of three-phase induction motors.
It’s a simple and cost-effective method that provides full voltage to the motor right from the start. The DOL starter is commonly used for motors with relatively small power ratings.
Here are the key components and features of a DOL starter:
-
Contactor: The DOL starter includes a contactor, which is an electromagnetic switch that controls the connection and disconnection of electrical power to the motor. The contactor has normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts.
-
Overload Relay: This is a protective device that is connected to the motor circuit to sense the current flowing through the motor. If the current exceeds a preset value (indicating an overload or a fault), the overload relay opens the contacts, de-energizing the contactor and disconnecting power to the motor.
-
Start Button: The DOL starter has a start button that, when pressed, energizes the contactor coil and closes the main contacts, applying full voltage to the motor.
-
Stop Button: The stop button is used to de-energize the contactor coil, open the main contacts, and stop the motor.
The basic operation of a DOL starter involves pressing the start button, which energizes the contactor coil, closes the main contacts, and applies full voltage to the motor.
The motor starts, and when the stop button is pressed or if an overload occurs, the contactor de-energizes, opening the main contacts and stopping the motor.
While the DOL starter is simple and commonly used, it has some drawbacks, such as the high inrush current during motor starting, which can cause voltage sags and mechanical stress on the motor.
For larger motors or applications where a soft start is desirable, alternative starting methods like star-delta starters or soft starters may be used.
dol starter diagram for A 3-Phase Motor
A Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is a common method used for starting 3-phase induction motors. It provides full voltage to the motor terminals right from the start, allowing the motor to reach full speed quickly. Here’s a simple diagram for a DOL starter for a 3-phase motor:
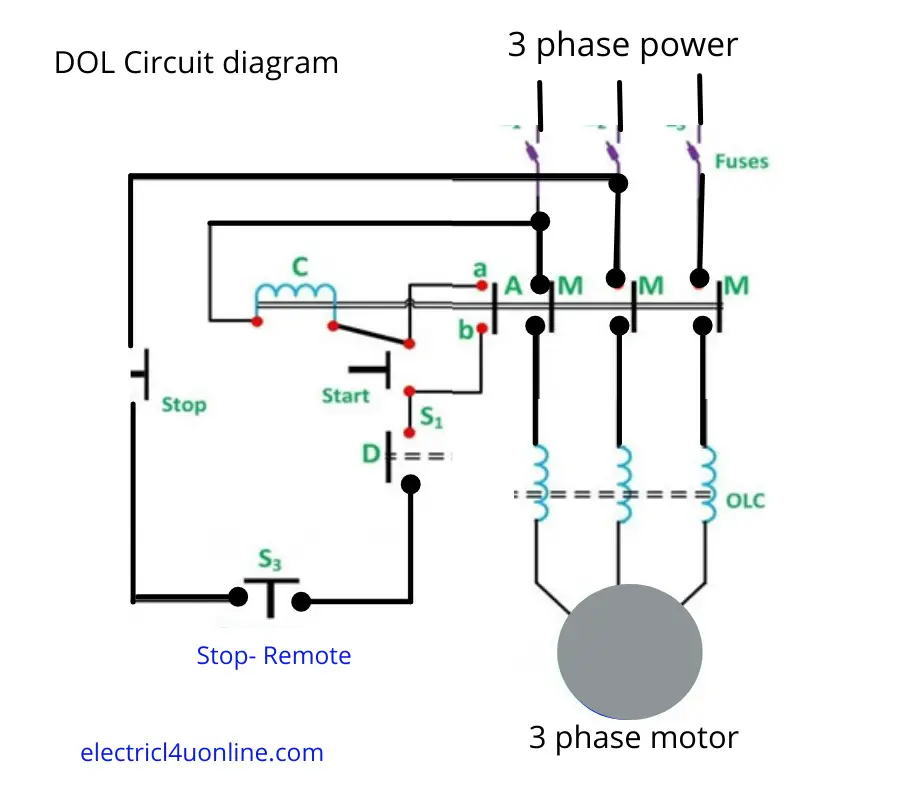
dol starter working
The Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is a simple and widely used method for starting three-phase induction motors. It provides full voltage to the motor terminals right from the start. The basic working principle of a DOL starter involves the following steps:
-
Start Button Pressed: When the start button is pressed, the main contactor coil (connected to the start button) is energized. This causes the main contacts of the contactor to close, allowing full voltage to be applied directly to the motor terminals.
-
Motor Energization: As the main contacts close, the full voltage is applied to the stator windings of the motor. This results in a high starting current, causing the motor to accelerate from a standstill to its rated speed.
-
Run Button Released: Once the motor has reached its rated speed, the run button can be released. The main contacts remain closed, and the motor continues to operate at the full supply voltage.
-
Stop Button Pressed: When the stop button is pressed, the main contactor coil is de-energized. This causes the main contacts to open, disconnecting the motor from the power supply and stopping the motor.
The DOL starter is suitable for small and medium-sized motors, but it has some disadvantages. The high starting current can cause voltage drops in the electrical supply system, and the sudden application of full voltage can result in mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment.
For larger motors, reduced-voltage starting methods such as star-delta starters or soft starters are often employed to mitigate these issues.
Why Do We Use A Contactor in DOL Starter?
A contactor is used in a Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter for several important reasons:
-
Switching High Currents: The main function of a contactor in a DOL starter is to control the electrical connection and disconnection between the power supply and the motor. When the motor is started, a high inrush current flows through the circuit. The contactor is designed to handle these high currents, ensuring reliable switching of the motor’s power supply.
-
Remote Control: A contactor allows for remote control of the motor. The start and stop buttons on the DOL starter panel are connected to the contactor coil. When the start button is pressed, the contactor coil is energized, closing the main contacts and supplying power to the motor. When the stop button is pressed or an overload condition is detected, the contactor coil is de-energized, opening the main contacts and disconnecting power from the motor.
-
Overload Protection: In a DOL starter, the contactor is often paired with an overload relay. The overload relay is connected to the motor circuit and is designed to trip and open the contactor’s main contacts if it detects an excessive current, indicating an overload or fault condition. This provides an additional layer of protection for the motor.
-
Reducing Control Circuit Power: Using a contactor allows the control circuit (the part of the circuit connected to the start and stop buttons) to handle lower currents. The control circuit operates at a lower voltage and is separate from the higher voltage circuit that powers the motor. This enhances safety and makes it easier to design and maintain the control system.
-
Durability and Longevity: Contactor components are designed to handle frequent switching operations. Using a contactor in the DOL starter ensures a reliable and durable switching mechanism for the motor, contributing to the overall longevity and reliability of the motor control system.
In summary, a contactor in a DOL starter serves as a robust and reliable switch for controlling the power supply to the motor.
It facilitates remote control, provides overload protection, and contributes to the safety and efficiency of the motor control system.
When DOL Starter Is A Good Choice?
A Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is a good choice for certain applications and motor sizes. Here are scenarios where a DOL starter is often suitable:
-
Small to Medium Motor Sizes: DOL starters are commonly used for small to medium-sized three-phase induction motors. These motors typically have power ratings ranging from fractional horsepower to several hundred kilowatts.
-
Simple Applications: DOL starters are well-suited for applications where a simple and cost-effective starting method is sufficient. Examples include pumps, fans, compressors, conveyors, and other similar machinery where the high inrush current during starting is acceptable.
-
Stable Power Supply: If the power supply system can handle the high inrush current associated with DOL starting without causing voltage sags or other issues, a DOL starter may be appropriate. This is typically the case in industrial settings with robust power distribution systems.
-
No Special Starting Requirements: When the motor and driven equipment can tolerate the mechanical stress and torque surge associated with the sudden application of full voltage, a DOL starter may be suitable. Some applications, especially those involving inertial loads, can handle the abrupt starting characteristics of a DOL starter.
-
Space Limitations: DOL starters are relatively compact and straightforward, making them suitable for installations with limited space. They consist of a contactor, overload relay, and a simple control circuit, making them easy to install and maintain.
Ultimately, the choice of a DOL starter depends on the specific requirements of the application, the characteristics of the motor, and the limitations or preferences of the electrical system.
It’s advisable to consider these factors and consult with electrical engineers or professionals when selecting the appropriate starting method for a given motor application.
Does the DOL Starter Reduce The Starting Current?
No, a Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter does not reduce the starting current of a motor. In fact, one of the characteristics of a DOL starter is that it applies the full line voltage directly to the motor terminals from the start. As a result, the motor experiences a high inrush current during the starting process.
The high inrush current can have several implications:
-
Voltage Sag: The sudden draw of a high current can cause a temporary drop in voltage, known as voltage sag, in the electrical system. This can affect other connected equipment and may not be suitable in situations where a stable power supply is crucial.
-
Mechanical Stress: The abrupt application of full voltage can lead to mechanical stress on the motor and the connected driven equipment. This stress can result in torque surges and may impact the overall mechanical integrity of the system.
-
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): The high inrush current can generate electromagnetic interference, potentially affecting other electronic devices or systems in the vicinity.
For these reasons, DOL starters are typically used for small to medium-sized motors in applications where the high inrush current and associated effects are acceptable.
In cases where reducing the starting current is desirable to minimize these effects, alternative starting methods such as soft starters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) are often employed.
Soft starters and VFDs allow for a controlled ramp-up of voltage and frequency, resulting in a gradual increase in motor speed.
This helps to reduce the inrush current, minimize voltage sags, and provide a smoother start for the motor.
These methods are particularly beneficial for larger motors and applications where the impact of high inrush current needs to be mitigated. For more information about motor starting methods, read my detailed article here.
How Do You Keep A DOL Starter Working Properly?
To ensure a Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter continues to work properly and reliably, regular maintenance and attention to certain factors are essential. Here are some guidelines to keep a DOL starter working effectively:
-
Regular Inspection:
- Conduct routine visual inspections of the DOL starter components, including the contactor, overload relay, and control wiring. Look for signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
- Ensure that all connections are secure and that there are no loose or damaged wires.
-
Overload Protection:
- Set the overload relay to the correct current rating for the motor it is protecting. This helps prevent damage to the motor in case of an overload.
- Periodically test the operation of the overload relay to ensure it responds appropriately to overload conditions.
-
Cleanliness:
- Keep the DOL starter and its surroundings clean. Dust and debris can accumulate on the components, affecting their performance and longevity.
- Clean the contactor contacts if they become dirty or show signs of arcing.
-
Tightening Connections:
- Periodically check and tighten all electrical connections, including those in the control circuit and power circuit. Loose connections can lead to overheating and may compromise the starter’s functionality.
-
Environmental Considerations:
- Ensure that the DOL starter is installed in a suitable environment. Extreme temperatures, humidity, or corrosive atmospheres can impact the performance and lifespan of the components.
-
Replace Worn Components:
- Replace any worn-out or damaged components promptly. This includes worn contactor contacts, malfunctioning start and stop buttons, and any other components showing signs of wear.
-
Documentation:
- Maintain accurate documentation, including the electrical schematic and manuals for the DOL starter. This can be helpful for troubleshooting and ensuring correct connections during maintenance.
-
Testing:
- Regularly test the DOL starter by initiating start and stop operations to ensure that the contactor engages and disengages properly.
- Perform periodic tests of the motor to check for any unusual sounds, vibrations, or other signs of potential issues.
-
Training and Awareness:
- Ensure that personnel responsible for the DOL starter are trained in its operation and maintenance.
- Encourage a culture of awareness, where operators report any unusual behavior or signs of malfunction promptly.
-
Compliance with Standards:
- Ensure that the DOL starter and its installation comply with relevant electrical standards and regulations.
Regular maintenance and attention to these factors can contribute to the reliable and efficient operation of a DOL starter, minimizing the risk of unexpected failures and prolonging its service life.
One of the most common contactors faults is phase failure; this means one contact phase is always closed, even if the contactor coil is de-energized. Read my article about contactor failure here.


