Table of Contents
Understanding Battery Connections: Series vs. Parallel
Batteries can be connected in two main ways: series and parallel. Each setup affects the overall voltage and current, so knowing the difference is important for choosing the right configuration for your needs.
Series Connection (Increasing Voltage)
- Batteries are linked end to end (positive to negative).
- The voltage adds up, meaning the total voltage is the sum of all batteries.
- The capacity (Ah) stays the same as a single battery.
- The current remains the same across all batteries.
- Used when higher voltage is needed, such as in electric vehicles or solar power systems.
Parallel Connection (Increasing Capacity)
- Batteries are connected side by side (all positives together, all negatives together).
- The voltage stays the same as a single battery.
- The capacity (Ah) increases, as all battery capacities combine.
- The current capacity increases, allowing more power to be drawn.
- Ideal for applications that need more energy storage, like backup power systems.
Choosing the Right Connection
- If you need a higher voltage, go for a series connection.
- If you need longer battery life (higher capacity), choose a parallel connection.
- For both high voltage and high capacity, a combination of series and parallel can be used.
Important Tip: Always use batteries of the same voltage and capacity to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
| Parameters | Batteries in Series | Batteries in Parallel |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Adds up (V_total = V_1 + V_2 + …) | Same as the voltage of a single battery |
| Current | Same across all batteries | Increases (A_total = A_1 + A_2 + …) |
| Capacity | Same as that of a single battery | Adds up (C_total = C_1 + C_2 + …) |
| Application | Increase total voltage for higher voltage needs | Increase total current for higher current requirements |
Parallel connection of batteries increases the current capacity Amp-hour output, While the voltage has no change.
connecting batteries in series Diagram
When connecting batteries in series, the positive terminal of one battery is linked to the negative terminal of the next. This setup increases the total voltage, while the capacity (Ah) remains the same as a single battery.
When we add two or more batteries, It is necessary that the Voltage and capacity rating of each battery must be the same.
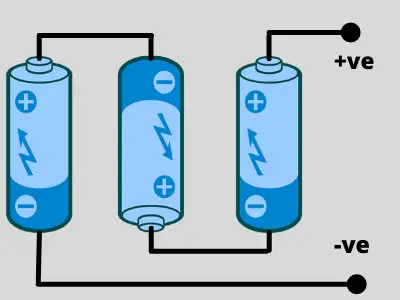
How to Connect Batteries in Series
Connecting batteries in series increases the total voltage while keeping the capacity the same. Follow these steps to do it correctly:
Gather the Batteries
- Make sure you have the required number of batteries with the same voltage and capacity for a safe connection.
Arrange the Batteries
- Place them side by side so that the positive terminal of one battery is next to the negative terminal of the next.
Connect the Batteries
- Use proper wires or connectors to link:
- The positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second.
- The positive terminal of the second battery to the negative terminal of the third, and so on.
Secure the Connections
- Ensure all connections are tight and secure to avoid loose wiring, which can cause power loss or safety hazards.
Test the Circuit
- Measure the voltage across the battery bank. The total voltage should be the sum of all battery voltages (e.g., three 12V batteries in series will give 36V).
Important Tip:
Always double-check the polarity—incorrect wiring can damage the batteries or cause short circuits.
connecting batteries in parallel Diagram
When connecting batteries in parallel, you essentially connect the positive terminals of all the batteries and the negative terminals of all the batteries.
This creates a battery bank where the positive and negative terminals are the overall positive and negative terminals of the entire bank. Here’s a step-by-step guide to connecting batteries in parallel:
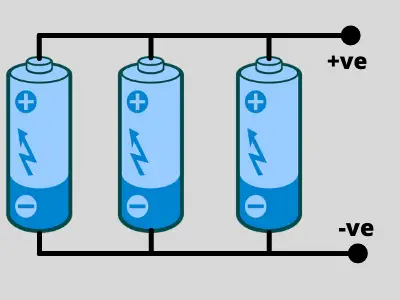
-
Gather the batteries: Collect the batteries you intend to connect in parallel.
-
Arrange the batteries: Position the batteries side by side in a row, ensuring that all the positive terminals and negative terminals are oriented in the same direction.
-
Connect the batteries: Use appropriate cables or wires to connect the positive terminals of all the batteries to each other and the negative terminals of all the batteries to each other. This creates a parallel connection among the batteries.
-
Secure the connections: Ensure that all the connections are secure and tight to prevent any loose connections or accidental disconnections.
-
Test the circuit: After connecting the batteries in parallel, test the circuit to ensure that the voltage remains the same as that of a single battery, while the overall current capacity increases.
When connecting batteries in parallel, make sure that the positive terminals are connected and the negative terminals are connected.
This configuration helps in increasing the overall current capacity of the battery bank without changing the voltage.
Also, it’s crucial to use batteries with the same voltage and capacity to ensure optimal performance and prevent any issues related to imbalances in charging and discharging.
Series / parallel connection
Series-parallel connections involve combining series and parallel configurations to create a more complex electrical circuit. This allows you to achieve specific voltage and current requirements for a particular application.
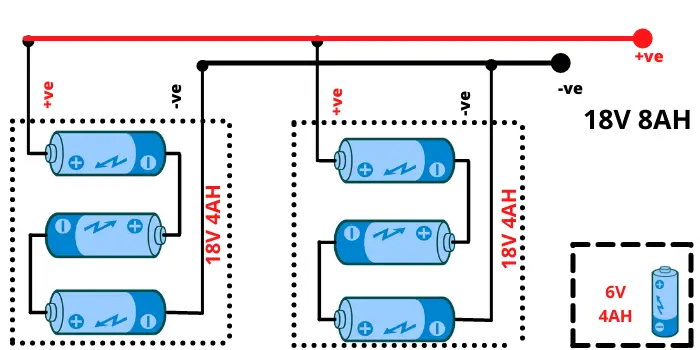
Conclusion:
Here is how you can set up a series-parallel connection:
-
Understand the requirements: Determine the specific voltage and current requirements for your application. If you need both increased voltage and current, a series-parallel connection may be the solution.
-
Group the batteries: Divide the batteries into smaller groups, each with the required number of batteries to achieve the desired voltage and current output.
-
Connect the groups in parallel: Connect the positive terminals of the groups together and the negative terminals of the groups together to create separate parallel circuits.
-
Connect the groups in series: Connect the positive terminal of the first parallel group to the negative terminal of the next parallel-group, and so on until all the groups are connected in a series.
-
Secure the connections: Ensure that all connections are secure and properly insulated to prevent any short circuits.
-
Test the circuit: After setting up the series-parallel connection, test the circuit to verify that the voltage and current levels meet the requirements of your application.
Series-parallel connections are often used in various applications, such as in electric vehicles, solar power systems, and other high-power applications where specific voltage and current levels are necessary.
battery series connection formula
When batteries are connected in series, the total voltage across the series connection is the sum of the individual voltages of each battery. The formula for calculating the total voltage in a series connection of n batteries is:
V total=V1+V2+…+Vn,
where:
- Vtotal is the total voltage across the series connection,
- V1, V2,…, Vn are the voltages of the individual batteries in the series connection.
For example, if you have three batteries with voltages 6 volts, 8 volts, and 10 volts connected in series, the total voltage across the series connection would be:
V total=6 V+8 V+10 V=24 V.
Make sure to use the appropriate units for voltage, such as volts (V). This formula helps in understanding how the voltage adds up when batteries are connected in series.
batteries in the parallel formula
When batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage across the parallel connection remains the same as that of a single battery. However, the overall capacity increases. The formula for calculating the total capacity in a parallel connection of batteries is:
C_total=C1+C2+…+Cn
where:
- C total is the total capacity across the parallel connection,
- C1, C2,…, Cn are the capacities of the individual batteries in the parallel connection.
For example, if you have three batteries with capacities of 1000 mAh, 1200 mAh, and 1500 mAh connected in parallel, the total capacity across the parallel connection would be:
C total = 1000 mAh+1200 mAh+1500 mAh = 3700 mAh
Ensure that all capacities are in the same units, such as milliampere-hours (mAh). This formula illustrates how the capacity adds up when batteries are connected in parallel.
Don’t Leave Empty-Handed!
Install my Free Android App on Google Play:
Electrical Cables Most Common Tables “Cables Tables”
And, my Electrical Calculations App “Fast Electrical Calculator”
Discover more great content by subscribing to My channel
Looking to stay ahead of the game in the world of electrical engineering? Subscribe to my YouTube channel and gain access to exclusive content you won’t find anywhere else!
The staff I recommend
(Amazon Affiliate Links to products I believe are high quality):
- Economy 120 Volt/60Hz AC Power Source – Step-Down Voltage & Frequency Converters 1800W
- UNI-T Digital Multimeter Tester UT139C
- 50-Amp Extension Cord for RV “100ft”
- Voltage Stabilizer 110/220v
- Hair Dryer “best selling“
- TOSHIBA EM131A5C-BS Countertop Microwave Ovens
Disclaimer: This contains affiliate links to Amazon products. I may earn a commission for purchases made through these links.





